Difference between MultiProcessor and Multicore Processor?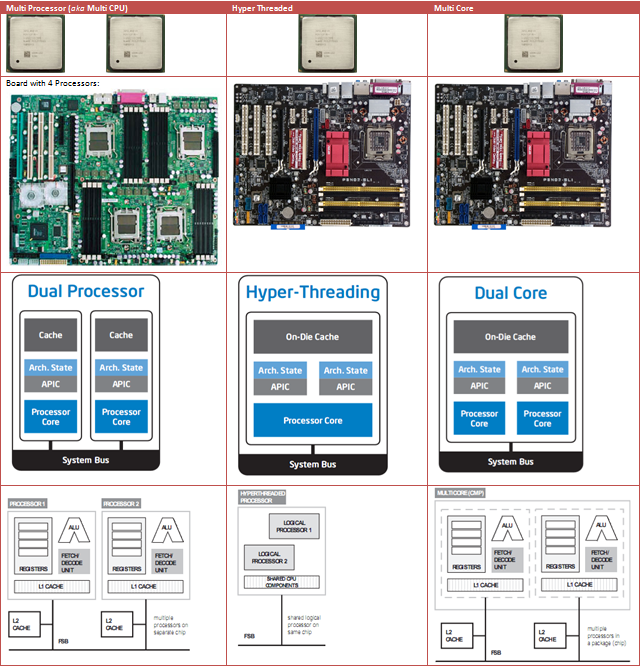
A multiprocessor system contains more than one CPU, allowing them to work in parallel.
A multicore CPU has multiple execution cores on one CPU so that multiple cores can work in parallel on separate operations at chip level.
Difference between MultiProgramming, MultiTasking, MultiProcessing, MultiThreading?
MultiProgramming:
To minimize the CPU Idle time, Multiprogramming was introduced in older days for single core processor. One or more programs are loaded into main memory which are ready to execute still, only one program is able to get the CPU for execution while all others are waiting for their turn. When currently running process is performing an I/O task, then OS may interrupt that process and give the control to another program(process context switching) loaded in main memory for execution and a running process keeps executing until either it voluntarily releases the CPU or when it blocks for an I/O operation.
With MutilProgramming, OS should perform decision making as multiple jobs now needed to be loaded into memory at the same time and several options existed for allocating CPU time.
To handle Decision making two types of scheduling were introduced
Job Scheduling – refers to the selection of jobs to load into memory.
CPU scheduling – refers to the selection of a job existing in memory to execute via the CPU.
Another issue that needs to be handled as well is that large programs may not fit at once in memory which was solved by using pagination and virtual memory.
MultiTasking:
Multitasking has the same meaning of multiprogramming but in a more general sense, it is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks (processes) over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as CPU and main memory.
The concept of multitasking is that the CPU time is shared equally among the processes or tasks. In multiprogramming (older OS) one program as a whole keeps running until it blocks or ends, in multitasking (modern OS) time-sharing is best manifested because each running process takes only a fair quantum of the CPU time.
For example, Consider that 3 tasks are loaded into the main memory and time allocated for each program is 3 microseconds. Now the first task executing, after 3 microseconds irrespective whether the task gets completed or not it gets switched to the second task. Similarly, after 3 microseconds it goes to the third task. Thus the CPU time is shared equally among the tasks.
Multitasking takes place in a single processor or sometimes multiprocessor and multitasking does not require parallel execution of multiple tasks at exactly the same time instead, it allows more than one task to advance over a given period of time. Even on multiprocessor computers, multitasking allows many more tasks to be run than there are CPUs.
MultiThreading
Multithreading is thread-based multitasking.
The basic difference between multitasking and multithreading is that in multitasking, the system allows executing multiple programs and tasks at the same time, whereas, in multithreading, the system executes multiple threads of the same or different processes at the same time.
In multitasking, CPU has to switch between multiple programs so that it appears that multiple programs are running simultaneously. On other hands, in multithreading CPU has to switch between multiple threads to make it appear that all threads are running simultaneously.
Multitasking allocates separate memory and resources for each process/program whereas, in multithreading threads belonging to the same process shares the same memory and resources as that of the process.
MultiProcessing
Multiprocessing refers to the hardware (i.e., the CPU units) rather than the software (i.e., running processes). If the underlying hardware provides more than one processor then that is multiprocessing.
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more CPUs (processors) within a single Computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor within a single computer system. Now since there are multiple processors available, multiple processes can be executed at a time. These multiprocessors share the computer bus, sometimes the clock, memory and peripheral devices also.
Multiprocessing system’s working –
- With the help of multiprocessing, many processes can be executed simultaneously. Say processes P1, P2, P3, and P4 are waiting for execution. Now in a single processor system, firstly one process will execute, then the other, then the other and so on.
- But with multiprocessing, each process can be assigned to a different processor for its execution. If its a dual-core processor (2 processors), two processes can be executed simultaneously and thus will be two times faster, similarly a quad-core processor will be four times as fast as a single processor.
Why use multiprocessing –
- The main advantage of a multiprocessor system is to get more work done in a shorter period of time. These types of systems are used when very high speed is required to process a large volume of data. Multiprocessing systems can save money in comparison to single processor systems because the processors can share peripherals and power supplies.
- It also provides increased reliability in the sense that if one processor fails, the work does not halt, it only slows down. e.g. if we have 10 processors and 1 fails, then the work does not halt, rather the remaining 9 processors can share the work of the 10th processor. Thus the whole system runs only 10 percent slower, rather than failing altogether.
Difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous programming.
Synchronous Programming
Program execution in most high-level languages is usually very straightforward. Your program starts at the first line of source code and each line of code executed sequentially thereafter. Synchronous program execution is somewhat similar to the above. Your program is executed line by line, one line at a time. Each time a function is called, program execution waits until that function returns before continuing to the next line of code.
Suppose a function is called to start a time-consuming process, the whole application has to wait until it finishes, this is a disadvantage of synchronous programming.
Asynchronous Programming is a form of parallel programming that allows a unit of work to run separately from the primary application thread. When the work is complete, it notifies the main thread (as well as whether the work was completed or failed). There are numerous benefits to using it, such as improved application performance and enhanced responsiveness.
Suppose a time-consuming process is called, the application doesn’t wait for this to complete and continue executing next instructions sequentially, this process notifies the application thread or main thread after it completes.
For more references:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/operating-system-difference-multitasking-multithreading-multiprocessing/
https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-multithreading-and-vs-multitasking/
https://gabrieletolomei.wordpress.com/miscellanea/operating-systems/multiprogramming-multiprocessing-multitasking-multithreading/
https://superuser.com/questions/214331/what-is-the-difference-between-multicore-and-multiprocessor